A PESTEL analysis provides companies with a comprehensive overview of the external environmental factors that can affect their business. This method of analysis is important not only for creating a solid business plan, but also for long-term strategic planning in day-to-day operations. In this article, I will explain how a PESTEL analysis is performed and give you practical examples from a fictitious PESTEL analysis. Learn how this analysis can help you maintain your competitiveness and gain competitive advantage.
Definition: What is the PESTEL analysis?
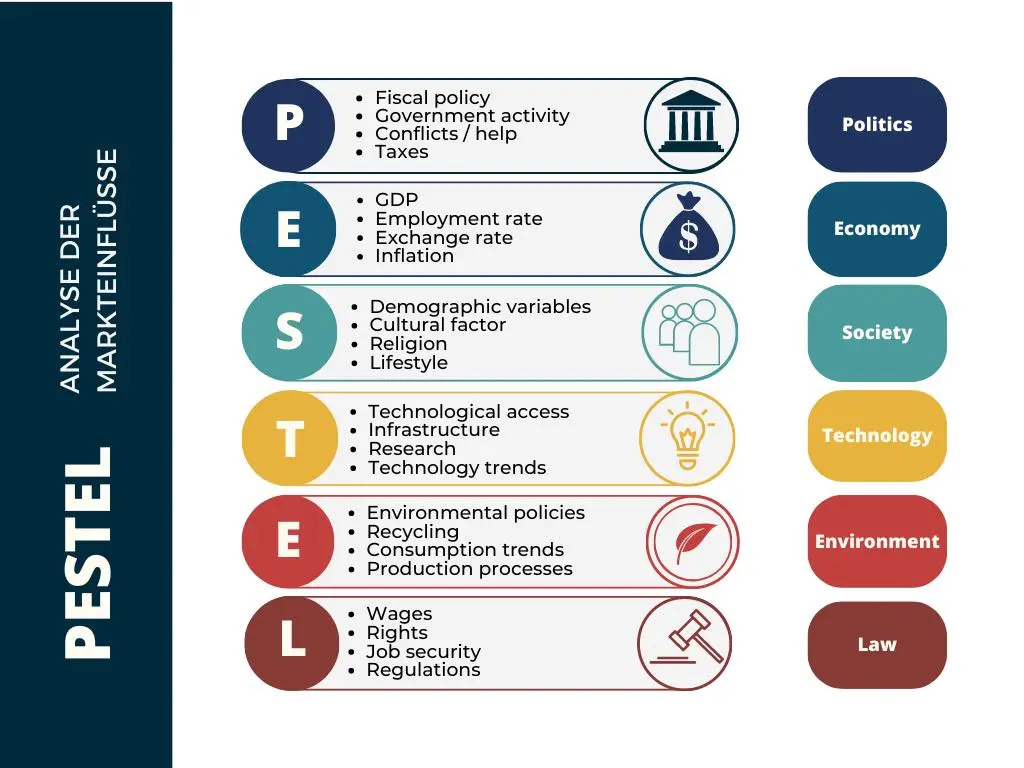
The PESTEL analysis is based on six main factors, which are summarized in the acronym “PESTEL”:
• Political
• Economic
• Social
• Technological
• Environmental
• Legal
These six factors form the basic framework of the PESTEL analysis and make it possible to examine the relevant external factors influencing a company.
This method of analysis enables companies to understand the impact of these factors on their business. In the start-up phase of a company, the PESTEL analysis is often used as part of a SWOT analysis to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and potential threats.
PESTEL analysis takes into account external factors that affect the business and are largely outside the control of the entrepreneur. The combination of SWOT and PESTEL creates a holistic picture that serves as a solid basis for management decisions and from which recommendations for action can be derived. This analysis helps maximize opportunities for success and minimize risks.
Origin of PESTEL analysis
The origins of PESTEL analysis are not entirely clear, but it is believed to have been developed in the 1960s and 1970s as a tool for analyzing the external environment as part of strategic planning. Francis J. Aguilar, a professor at Harvard Business School, published Scanning the Business Environment in 1967, which established the PESTEL analysis of economic, technical, political, and social influences. Arnold Brown of the American Institute of Life Insurance developed the STEP analysis (Strategic Trend Evaluation Process) from this. Later, the PEST analysis evolved into the PESTEL analysis by adding environmental and legal factors to the original four factors-political, economic, sociocultural, and technological influences. PESTEL analysis is now a widely used and effective tool for strategic analysis that can help companies remain competitive in a rapidly changing business environment.
Political factors
Political factors are influenced by the actions and decisions of the government. These factors can have a significant impact on businesses. Political factors include, but are not limited to, the following.
- Regulatory framework: Laws, ordinances and regulations that affect business activities.
- Tax policy: Changes in tax laws and policies that may affect the financial situation of companies.
- Trade Agreements: International trade agreements and relationships that affect market access and international competition.
- Political stability: A country’s political situation can have an impact on investments, business relationships and the general business climate.
Example of a political factor: A government passes new environmental laws that impose strict emissions standards on companies. This forces companies to adapt their production processes to comply with the new regulations and meet environmental requirements.
The political factors in a PESTEL analysis can have a significant impact on a company’s strategic direction and long-term planning. By analyzing and understanding these factors, companies can better respond to policy changes and maintain their competitiveness.
Economic factors
Economic factors refer to the financial aspects of the general economy. They generally include
- Interest rates: The level of interest rates influences the cost of credit and the investment behavior of companies.
- Employment rates: The situation on the labor market and the unemployment rate affect consumption and demand.
- Inflation: The development of prices and the inflation rate influence the purchasing power of consumers and the profit margins of companies.
- Exchange rates: Exchange rate fluctuations affect international trade and the competitiveness of companies.
Financial analysts in the financial sector often pay particular attention to economic factors because they are easier to quantify and model than some other factors in the PESTEL analysis, which are more qualitative in nature.
Example of an economic factor: If the economy is in recession and government bond yields are falling, an equity analyst may adjust the discount rate in his model assumptions. This can have a significant impact on the company valuations it analyzes.
Economic factors play an important role in the analysis and valuation of companies. By carefully monitoring these factors, companies can better respond to economic changes and adjust their business strategy accordingly.
Social factors
Social factors are often more difficult to quantify than economic factors and relate to changes in lifestyles, attitudes, and demographic characteristics. They can have a significant impact on economic activities. Examples of social factors are
- Demographic factors: Age, gender, ethnicity and other demographic characteristics influence consumption habits and preferences.
- Lifestyle trends: Changes in the way people live, work, communicate and spend their leisure time influence demand for products and services.
- Consumer beliefs: Consumer attitudes, values and beliefs influence purchasing behavior and demand for specific products.
- Attitudes toward working conditions: Changes in employee expectations regarding working hours, flexibility, work-life balance and corporate culture influence employee attitudes and retention.
Social factors may seem insignificant compared to measurable variables such as interest rates or taxes, but they still have a significant impact on entire industries. For example, changing attitudes toward healthy and active lifestyles have led to a boom in connected fitness technologies and demand for healthy foods.
Example of a social factor: After the COVID-19 pandemic, management at a technology company had to rethink its hiring, onboarding, and training practices because many employees preferred a hybrid model in which they worked from home. This reflected the change in attitudes toward the work environment and work-life balance.
Social factors play an important role in analyzing consumer behavior and adapting business strategies to changing social trends and preferences.
Technological factors
In today’s business world, technology is ubiquitous and rapidly changing. Both management teams and analysts need to understand the impact of technological factors on companies and industries. Here are some examples of technological factors:
- Digitization and automation: Advances in digital technology are enabling greater automation of processes and business operations, leading to efficiency gains and cost savings.
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning: the application of AI and ML in various areas such as customer service, data analytics and personalized recommendations opens up new opportunities and changes business models.
- Technological infrastructure: The availability of fast Internet connections, next-generation mobile networks (e.g., 5G) and modern IT infrastructures influences the performance of companies and enables new innovative applications.
- Data security and data protection: In view of increasing threats from cybercrime, ensuring data security and data protection is of paramount importance in order to maintain customer trust and meet legal requirements.
Example of a technological factor: A retail company invests in the implementation of an advanced e-commerce system and a user-friendly mobile application to facilitate customer access and improve the online shopping experience.
Technological factors have a significant impact on the business landscape. Companies that actively follow technological developments and implement corresponding strategies can increase their competitiveness, open up new markets and develop innovative solutions for their customers.
Environmental factors
Environmental factors are a key component of PESTEL analysis and capture the impact of the physical environment on businesses. They are playing an increasingly important role as companies increasingly recognize that environmental changes can bring both risks and opportunities. The following are some examples of environmental factors
- Climate change: changes in climatic conditions such as rising temperatures, more frequent extreme weather events, and rising sea levels.
- Energy consumption and efficiency: The sustainability and efficiency of the energy sources a company uses and how to increase energy efficiency in business processes.
- Resource use and management: The responsible use and protection of natural resources such as water, soil, raw materials and biodiversity.
- Environmental laws and regulations: Compliance with environmental standards, laws and regulations that may affect business operations.
Example of an environmental factor: A company in the food industry needs to rethink its packaging strategy to find more environmentally friendly alternatives to single-use plastic and promote the circular economy.
Considering environmental factors in a PESTEL analysis enables companies to adapt to environmental changes, achieve their sustainability goals, and identify opportunities related to environmentally conscious innovation and customer preferences. At the same time, they can minimize risks such as regulatory measures and reputational damage caused by environmentally harmful behavior.
Legal factors
Legal factors are a key component of the PESTEL analysis and refer to changes in the legal environment that may affect companies and industries. Here are some examples of legal factors
- Tax laws and regulations: Changes in corporate taxation and tax laws can have a financial impact on companies.
- Labor law: Laws and regulations on working conditions, employment contracts, minimum wages and occupational health and safety can affect operating costs and relations between employers and employees.
- Trade agreements and tariffs: Changes in trade agreements and tariffs can affect cross-border trade and have an impact on import and export activities.
- Data protection laws: Regulations on the protection of personal data can govern the way companies collect, store and process data and influence the way they handle customer data.
Example of a legal factor: A company operating in e-commerce must deal with the data protection provisions of the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and ensure that it takes the necessary measures to protect customer data in order to avoid legal consequences and reputational damage.
Considering legal factors in a PESTEL analysis enables companies to identify legal risks and opportunities, adapt to legal requirements, and align their business strategies accordingly. It is important to monitor relevant laws and regulations and consider the legal framework when making business decisions.
How can the PESTEL analysis be used in Human Resource?
PESTEL analysis also provides valuable insights in the area of human resources (HR), helping companies understand the impact of external environmental factors on their HR strategy and practices. Below are some ways in which PESTEL analysis can be used in HR:
1) Political factors: By analyzing political factors such as labor laws, immigration policies, or minimum wage regulations, companies can understand the legal framework governing their recruitment, compensation structures, and employee relations. This enables them to adapt their HR practices accordingly and ensure compliance.
2) Economic factors: The analysis of economic factors such as unemployment rate, inflation or wage development offers insights into the labor market and economic stability. Companies can use this information to optimize their workforce planning, adjust salary structures and develop appropriate incentive programs.
3) Societal factors: Taking into account societal factors such as demographic trends, changing values or employee expectations enables companies to align their HR strategy with the needs and preferences of their employees. This can include introducing flexible working time models, promoting diversity and inclusion, or creating a positive corporate culture.
4) Technological factors: The PESTEL analysis enables companies to assess the impact of technological developments on their HR processes. These include the use of HR software and tools, the automation of HR tasks, the promotion of digital skills among employees, and the consideration of data protection and cybersecurity aspects.
5) Environmental factors: The increasing sensitivity to environmental issues also requires corresponding measures in the HR area. By considering environmental aspects in the PESTEL analysis, companies can further develop their sustainability strategy, promote environmentally friendly work practices, and motivate employees to behave in an environmentally conscious manner.
6) Legal factors: The analysis of legal factors enables companies to assess the impact of labor laws, data protection regulations and other legislation on their business activities. This includes compliance with labor law, the promotion of equal opportunities and diversity, and the implementation of data protection measures.
By applying PESTEL analysis to HR, companies can adapt their HR strategy to changing environmental factors, secure competitive advantage, and ensure effective employee retention and development. It is important to review the analysis regularly and incorporate the results into long-term workforce planning.
Practical examples for the application of the PESTEL analysis
The use of PESTEL analysis allows companies to make a comprehensive assessment of the environmental factors that affect their operations. Here are some practical examples of the application of PESTEL analysis:
- A retail company uses PESTEL analysis to evaluate the political factor. It studies the impact of trade agreements on its international supply chains and the import of products. Based on this analysis, the company can make informed decisions about diversifying its supplier base and minimize potential trade risks.
- A technology company applies PESTEL analysis to analyze the economic factor. It studies employment rates and income levels in different regions to identify new markets for its products. Based on the results of the analysis, the company decides in which countries it would like to strengthen its sales and marketing activities.
- A healthcare company uses PESTEL analysis to look at the social factor. It analyzes demographic changes and the shift in consumer health consciousness. Based on this analysis, the company is developing new products and services that address the needs of an aging population and the growing trend toward healthy lifestyles.
- A utility company conducts the PESTEL analysis to study the technological factor. It analyzes the use of renewable energy technologies and the development of energy efficiency standards. Based on the results of this analysis, the company decides which technologies to invest in and which sustainable energy solutions to offer its customers.
- A hotel group uses PESTEL analysis to evaluate the environmental related factor. It analyzes environmental impacts such as energy and water consumption, waste management and the use of sustainable building materials. Based on the results of this analysis, the company is developing an environmentally friendly operating strategy to reduce costs and meet customer demand for sustainable accommodations.
These real-world examples show how companies can apply PESTEL analysis in a variety of industries and functions. By systematically analyzing PESTEL factors, companies can make informed decisions, adapt their strategies, and gain competitive advantage.
Alternatives to PESTEL Analysis
There are several alternatives to PESTEL analysis that can be used for strategic analysis. Here are some examples:
- SOAR Analysis: SOAR analysis is a positive alternative to SWOT analysis and focuses on strengths, opportunities, aspirations, and outcomes. Rather than focusing on weaknesses and threats, SOAR analysis focuses on positives and opportunities to realize full potential.
- DEEPLIST analysis: The DEEPLIST analysis is an alternative to the PESTEL analysis and examines demographic, economic, environmental, political, legal, informational, sociocultural, and technological factors. It expands the scope of the analysis and enables a more detailed examination of various dimensions of the business environment.
- Porter’s Five Forces: Porter’s Five Forces is a framework for analyzing competitive forces in an industry. It examines the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of suppliers and buyers, the threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of competition. The focus of this model is on industry and competitive analysis.
- SCORE Analysis: SCORE analysis stands for Strengths, Challenges, Options, Responses, and Evaluation. This tool is used to evaluate strategic options and make decisions. It helps identify strengths and weaknesses, assess potential challenges, develop options, identify appropriate responses, and evaluate results.
- Scenario planning: Scenario planning involves developing various future scenarios and analyzing their impact on the organization. This approach enables companies to prepare for various possible future developments and to develop appropriate strategies.
It is important to note that these alternatives to PESTEL analysis do not have to be used exclusively, but can also be used in combination. Companies can use different models and frameworks to gain a more comprehensive understanding of their environment and make informed strategic decisions. The choice of the appropriate method depends on the specific requirements, goals and framework conditions of the company.
Conclusion
The PESTEL analysis is a powerful tool that helps companies identify and assess the key environmental factors that can affect their business. By systematically examining political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal factors, companies gain valuable insights that enable them to make informed strategic decisions and identify opportunities and risks.
PESTEL analysis provides a holistic perspective on a company’s external environment and enables the identification of trends, changes and potential influencing factors. It helps companies build on their strengths, overcome their weaknesses and improve their competitive position. By understanding the impact of political decisions, economic developments, social changes, technological advances, environmental factors and legal frameworks, companies can be proactive and adapt their business strategy.
The PESTEL analysis is not only used to develop a solid business plan, but also for long-term strategic planning and to secure competitive advantages. It enables companies to adapt to the challenges of a dynamic business environment and respond to the needs and expectations of their stakeholders. It also helps companies implement responsible business practices, achieve their sustainability goals and meet changing customer needs.
Overall, PESTEL analysis is an indispensable tool for companies to develop a comprehensive understanding of their external environment and provide the basis for informed decision-making and strategic planning. By systematically examining the PESTEL factors, companies can minimize risks, exploit opportunities and open up new markets. PESTEL analysis is an indispensable tool for companies to operate successfully and achieve their goals in a constantly changing business environment.
Marketing books that develop you professionally and personally
They exist, the best marketing books in the world. If you want to learn from the best of the best, I have just the books. They inspired me from the ground up, let’s see what great ideas will come to you as you read the books.
Frequently asked questions and answers about PESTEL analysis
What is a PESTEL analysis?
PESTEL analysis is a strategic tool for analyzing the external macro-environmental factors that affect an organization. The acronym stands for political, economic, socio-cultural, technological, environmental and legal factors.
Who invented the PESTEL analysis?
The origins of PESTEL analysis are not entirely clear, but it is believed to have been developed in the 1960s and 1970s. Francis J. Aguilar, a professor at Harvard Business School, published Scanning the Business Environment in 1967, which established ETPS analysis of economic, technical, political, and social influences. Arnold Brown of the American Institute of Life Insurance then developed it further into STEP analysis, which stands for “Strategic Trend Evaluation Process.” Later, the PEST analysis was developed into the PESTEL analysis by adding environmental and legal factors to the original four factors-political, economic, sociocultural, and technological influences.
What are the advantages of PESTEL analysis?
PESTEL analysis can help companies remain competitive in a rapidly changing business environment by identifying opportunities and threats that may impact their operations and developing strategies to mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities. It can also help companies understand the external factors that may impact their operations and make informed decisions about future investments and expansions.
What are some alternatives to PESTEL analysis?
Some alternatives to PESTEL analysis are SOAR analysis, DEEPLIST analysis, Porter’s Five Forces analysis, SCORE analysis, and scenario planning.
What are the steps in performing a PESTEL analysis?
Steps in conducting a PESTEL analysis include identifying the political, economic, sociocultural, technological, environmental, and legal factors that may impact the business, examining and analyzing each factor, and developing strategies to mitigate risks and take advantage of opportunities.
Who typically performs a PESTEL analysis?
Companies and organizations of all sizes and industries can conduct a PESTEL analysis. It is often used by strategic planners, marketing teams, and business analysts to gain a better understanding of the external environment and make informed decisions about future investments and expansions.
How can the PESTEL analysis help in the development of a marketing strategy?
PESTEL analysis can help in developing a marketing strategy by helping companies identify external factors that may influence their marketing strategy. For example, the analysis can identify political, economic, and sociocultural factors that may have an impact on the target audience and their purchasing decisions. Companies can then adjust their marketing strategy to take these factors into account and better reach their target audience.
How often should a PESTEL analysis be performed?
The frequency with which a PESTEL analysis should be performed depends on the industry and business environment. As a rule, it is recommended that the analysis be performed at least once a year to ensure that companies can respond to changes in the environment and adjust their strategies accordingly.
What are examples of policy factors that should be considered in a PESTEL analysis?
Some examples of political factors that should be considered in a PESTEL analysis are regulations, laws, and political instability. For example, changes in tax legislation or trade agreements can have an impact on companies’ business activities.
How can companies use the results of a PESTEL analysis to adjust their strategies?
Companies can use the results of a PESTEL analysis to adjust their strategies by responding to opportunities and threats identified by external factors. For example, companies can adapt their marketing strategy to respond to changes in their target audience or in the economy.
What are examples of technological factors that should be considered in a PESTEL analysis?
Some examples of technological factors that should be considered in a PESTEL analysis are innovation, automation, and availability of technology. For example, the introduction of new technologies can impact a company’s business processes and create new opportunities for innovation and growth.
How can companies ensure that their PESTEL analysis is comprehensive?
Companies can ensure that their PESTEL analysis is comprehensive by conducting thorough research and consulting with experts in various fields. It is also important to ensure that all relevant factors are identified and analyzed to provide a complete picture of the external environment.










0 Comments